Hebbia
Founded Year
2020Stage
Incubator/Accelerator | AliveTotal Raised
$161.1MRevenue
$0000Mosaic Score The Mosaic Score is an algorithm that measures the overall financial health and market potential of private companies.
+177 points in the past 30 days
About Hebbia
Hebbia offers tools that use generative artificial intelligence to assist with workflows, analyze documents, and provide insights. It serves industries such as asset management, legal, real estate, and corporate consulting, offering artificial intelligence (AI) solutions for their needs. It was founded in 2020 and is based in New York, New York.
Loading...
Hebbia's Product Videos
_thumbnail.png?w=3840)
_thumbnail.png?w=3840)
ESPs containing Hebbia
The ESP matrix leverages data and analyst insight to identify and rank leading companies in a given technology landscape.
The AI investment intelligence platforms market develops AI-powered solutions that assist investors in research, analysis, and decision-making. These platforms leverage generative AI, copilots, machine learning, and advanced algorithms to analyze financial data, generate investment insights, predict market movements, and provide personalized investment strategies. By automating research processes …
Hebbia named as Challenger among 15 other companies, including Bloomberg, BlackRock, and Morningstar.
Hebbia's Products & Differentiators
Neural search
Hebbia empowers knowledge workers with neural search – eliminating work intensive information retrieval and unlocking diligence & analysis. Via one-click integration with major cloud storage providers, the platform syncs files to an end-to-end encrypted index. Users can query terabytes of unstructured information and surface passage-level results across every file type. Hebbia’s proprietary index & parse engines wrangle the most difficult data, and search scales independent of repository size.
Loading...
Research containing Hebbia
Get data-driven expert analysis from the CB Insights Intelligence Unit.
CB Insights Intelligence Analysts have mentioned Hebbia in 7 CB Insights research briefs, most recently on Aug 29, 2025.

Aug 29, 2025 report
Book of Scouting Reports: Generative AI in Financial Services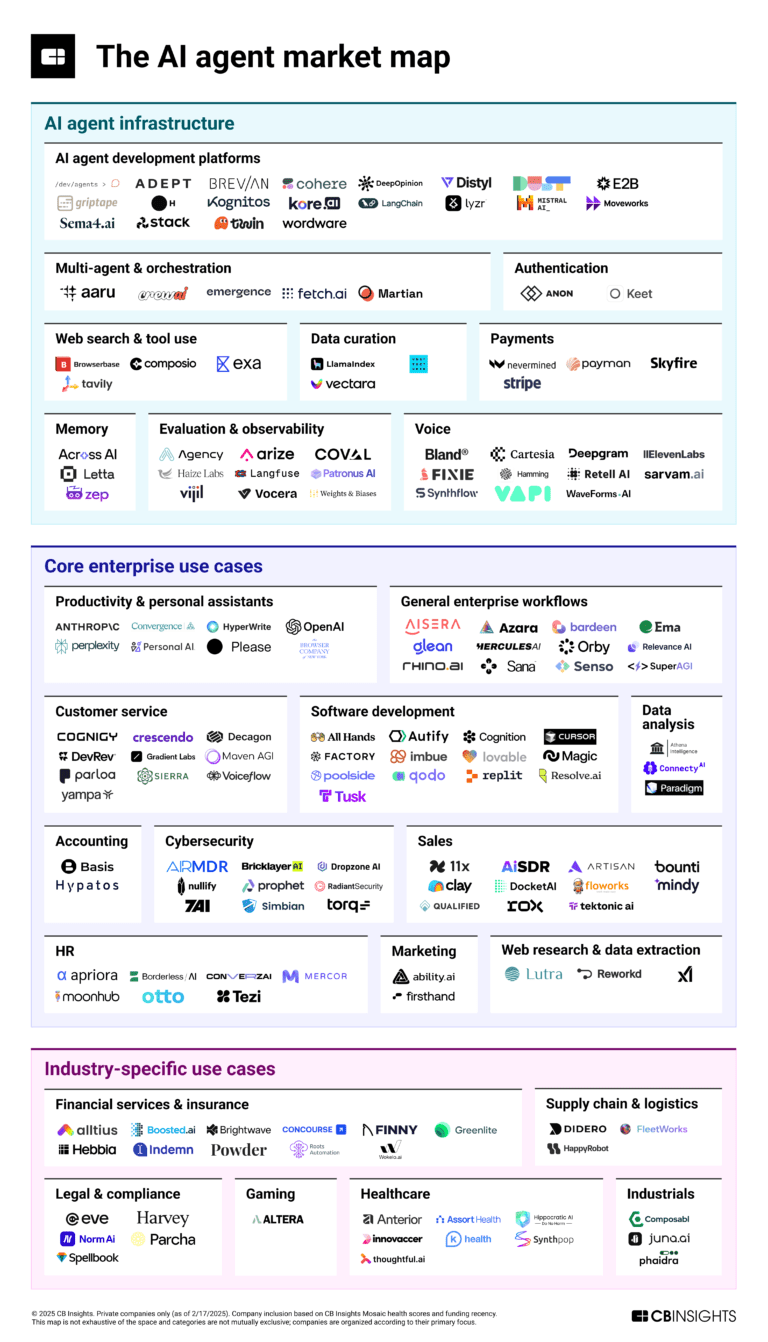
Mar 6, 2025
The AI agent market map
Aug 4, 2023
4 applications of generative AI in HRExpert Collections containing Hebbia
Expert Collections are analyst-curated lists that highlight the companies you need to know in the most important technology spaces.
Hebbia is included in 5 Expert Collections, including Generative AI 50.
Generative AI 50
50 items
CB Insights' list of the 50 most promising private generative AI companies across the globe.
Generative AI
2,826 items
Companies working on generative AI applications and infrastructure.
Artificial Intelligence
10,402 items
AI Agents & Copilots Market Map (August 2024)
322 items
Corresponds to the Enterprise AI Agents & Copilots Market Map: https://app.cbinsights.com/research/enterprise-ai-agents-copilots-market-map/
AI agents
376 items
Companies developing AI agent applications and agent-specific infrastructure. Includes pure-play emerging agent startups as well as companies building agent offerings with varying levels of autonomy. Not exhaustive.
Hebbia Patents
Hebbia has filed 1 patent.

Application Date | Grant Date | Title | Related Topics | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
11/26/2024 | 4/8/2025 | Grant |
Application Date | 11/26/2024 |
|---|---|
Grant Date | 4/8/2025 |
Title | |
Related Topics | |
Status | Grant |
Latest Hebbia News
Sep 9, 2025
September 9, 2025, 3:37 pm IDT “Tools part refers to the ability to add capabilities to the models… LLMs can’t do that on their own. They need tools to be able to perform those actions.” This foundational insight, articulated by Katia Gil Guzman of OpenAI’s Developer Experience team, sets the stage for a significant shift in AI development. During a recent OpenAI Build Hours session, Guzman, alongside Christine Jones from Startup Marketing, unveiled and demonstrated OpenAI’s new suite of built-in tools, designed to empower developers with unprecedented capabilities for scaling AI applications. These tools abstract away much of the underlying complexity, allowing large language models (LLMs) to interact with the real world directly and autonomously. The core innovation lies in bridging the inherent limitations of LLMs with practical, real-world functionalities. While LLMs excel at language understanding and generation, their knowledge is typically limited by their training data cutoff, and they lack native abilities to perform actions or access external, dynamic information. Built-in tools fundamentally change this paradigm. “Built-in part means you don’t have to code anything… you can just use it,” Guzman explained, highlighting the immediate accessibility and simplified integration that these hosted tools offer. This means developers can imbue their AI agents with powerful new skills without writing custom functions or managing complex infrastructure. One of the most immediate benefits is the ability to overcome LLM knowledge cutoffs. For instance, the **Web Search** tool grants models the capacity to query the internet for up-to-date information, sidestepping the temporal limitations of their training data. This is crucial for applications requiring current events, real-time data, or dynamic facts. Complementing this is **File Search**, which allows models to pull relevant information from uploaded documents or vector stores. This feature significantly simplifies the implementation of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), as developers no longer need to manually handle complex processes like chunking, embedding, and ranking proprietary data. “All of that can be automated with the File Search tool,” Guzman affirmed, underscoring the efficiency gains. Beyond information retrieval, built-in tools enable sophisticated interaction and computation. The **Model Context Protocol (MCP)** tool is particularly transformative, offering LLMs access to hundreds of remote MCP servers, effectively connecting them to a vast ecosystem of external applications and APIs, such as Shopify or Stripe. This allows models to perform actions like querying e-commerce inventories or checking financial balances. The **Code Interpreter** further expands this computational prowess, enabling models to generate and execute Python code directly within OpenAI’s infrastructure. This capability is invaluable for complex tasks such as data analysis, mathematical computations, and deep image understanding, allowing agents to process and derive insights from structured data. The true power of these built-in tools emerges from their seamless integration and interoperability. They foster the development of highly capable agentic workflows that can span multiple domains. Developers can combine Web Search for external data, MCP for online sales information (e.g., from Stripe), and Code Interpreter for analyzing offline sales data (e.g., from a CSV file) and visualizing trends. This multi-tool orchestration allows AI agents to tackle comprehensive tasks that would otherwise require extensive, bespoke coding. A live demonstration showcased the practical application of these tools in building a data exploration dashboard. The model, given a natural language query about sales data, intelligently leveraged Web Search for external market trends, utilized the Stripe MCP to retrieve online sales figures, and employed the Code Interpreter to analyze local CSV files containing offline sales data. It then generated visualizations, presenting a holistic view of the business performance. This capability was further illustrated by a customer spotlight on Hebbia, which utilizes web search for intricate finance and legal workflows, demonstrating tangible real-world impact. This evolution significantly lowers the barrier to entry for advanced AI development. “Once you give the model access to the tool, it can decide when and how to use it and we automatically add the tool result to the conversation context,” Guzman explained. This “all-in-one” approach, where OpenAI handles the execution and context management, democratizes the creation of sophisticated AI agents. Developers can now build more robust, dynamic, and context-aware applications with minimal coding, focusing their efforts on creative problem-solving rather than infrastructure plumbing.
Hebbia Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When was Hebbia founded?
Hebbia was founded in 2020.
Where is Hebbia's headquarters?
Hebbia's headquarters is located at 233 Spring Street, New York.
What is Hebbia's latest funding round?
Hebbia's latest funding round is Incubator/Accelerator.
How much did Hebbia raise?
Hebbia raised a total of $161.1M.
Who are the investors of Hebbia?
Investors of Hebbia include Plug and Play Fintech Accelerator, Index Ventures, Peter Thiel, Google Ventures, Andreessen Horowitz and 11 more.
Who are Hebbia's competitors?
Competitors of Hebbia include Metal, Tavily, BlueFlame AI, Auquan, Wokelo and 7 more.
What products does Hebbia offer?
Hebbia's products include Neural search and 4 more.
Loading...
Compare Hebbia to Competitors

Rogo is a company specializing in generative artificial intelligence (AI) for the financial services industry. Its main offerings include an enterprise AI platform designed to automate workflows, manage productivity, and facilitate data-driven decision-making for financial institutions. Rogo's platform is tailored to meet the specific needs of financial institutions, including investment banking, hedge funds, private equity, and asset management firms. It was founded in 2021 and is based in New York, New York.

Glean is an enterprise AI platform that provides tools for workplace productivity across various sectors. Its main offerings include AI-assisted search, custom generative AI applications, and management of AI agents. The platform is used by departments such as engineering, customer service, sales, and human resources, in industries including retail and financial services. It was founded in 2019 and is based in Palo Alto, California.

Maya AI provides artificial intelligence solutions across various business sectors. The company offers services to automate tasks, improve workflows, and provide data processing and integrative platforms. Maya AI serves sectors such as human resources, customer service, and regulatory compliance. Maya AI was formerly known as XiByte. It was founded in 2017 and is based in Tampa, Florida.

AlphaSense is a market intelligence and search platform that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP) technology to provide insights across various sectors. The company offers tools for financial research, including access to equity research, expert call transcripts, and the ability to integrate and analyze internal content alongside public data. AlphaSense serves the financial services, asset management, consulting, and corporate sectors with its market intelligence solutions. It was founded in 2011 and is based in New York, New York.
Multiply focuses on enhancing creative workflows through personalized assistance and AI integration within various business sectors. The company offers a platform that streamlines the creative process by providing customizable templates, workflow automation, and tools for consistent content creation without repetitive tasks. Multiply primarily serves sectors that require collaborative content creation, such as marketing agencies, branding agencies, and digital content teams. Multiply was formerly known as Fluent. It was founded in 2019 and is based in Stockholm, Sweden.

Mem is a company that focuses on AI knowledge management and organization within teams. Its main offerings include tools that help organize work such as meeting notes, projects, and knowledge bases, making them searchable and accessible. These services aim to improve collaboration and information retrieval for teams across various sectors. Mem was formerly known as Supernote. It was founded in 2019 and is based in Los Altos, California. Mem operates as a subsidiary of OpenAI.
Loading...